Memory Solutions
Overview
Innovations in memory infrastructure are poised to significantly improve the performance and cost effectiveness of main stream data center applications. Business applications are under significant pressure to collect, analyze, store and deliver time sensitive value to end customers while simultaneously driving down costs. These applications are drawing upon large quantities of global data sources - sensor data, historical data, location data, and customer specific data – all of which must be scrutinized in real time. Memory infrastructure innovation is occurring along two vectors: near memory innovations and far memory innovations. Near memory innovation improves business application performance by driving up the number of SoC and CPU memory channels and improving the bandwidth of those individual memory channels while enabling innovative and lower cost memory technologies to be connected seamlessly to the SoC. Far memory innovation delivers shareable pools of memory resources that both drive up aggregate system memory utilization (and therefore drive down cost) and improve application performance as arrays of SoC devices can simultaneously operate on the shared memory pool. Memory infrastructure encompasses a broad range of new and emerging media types and interface technologies.
Figure 1: CXL and OMI Near Memory Innovation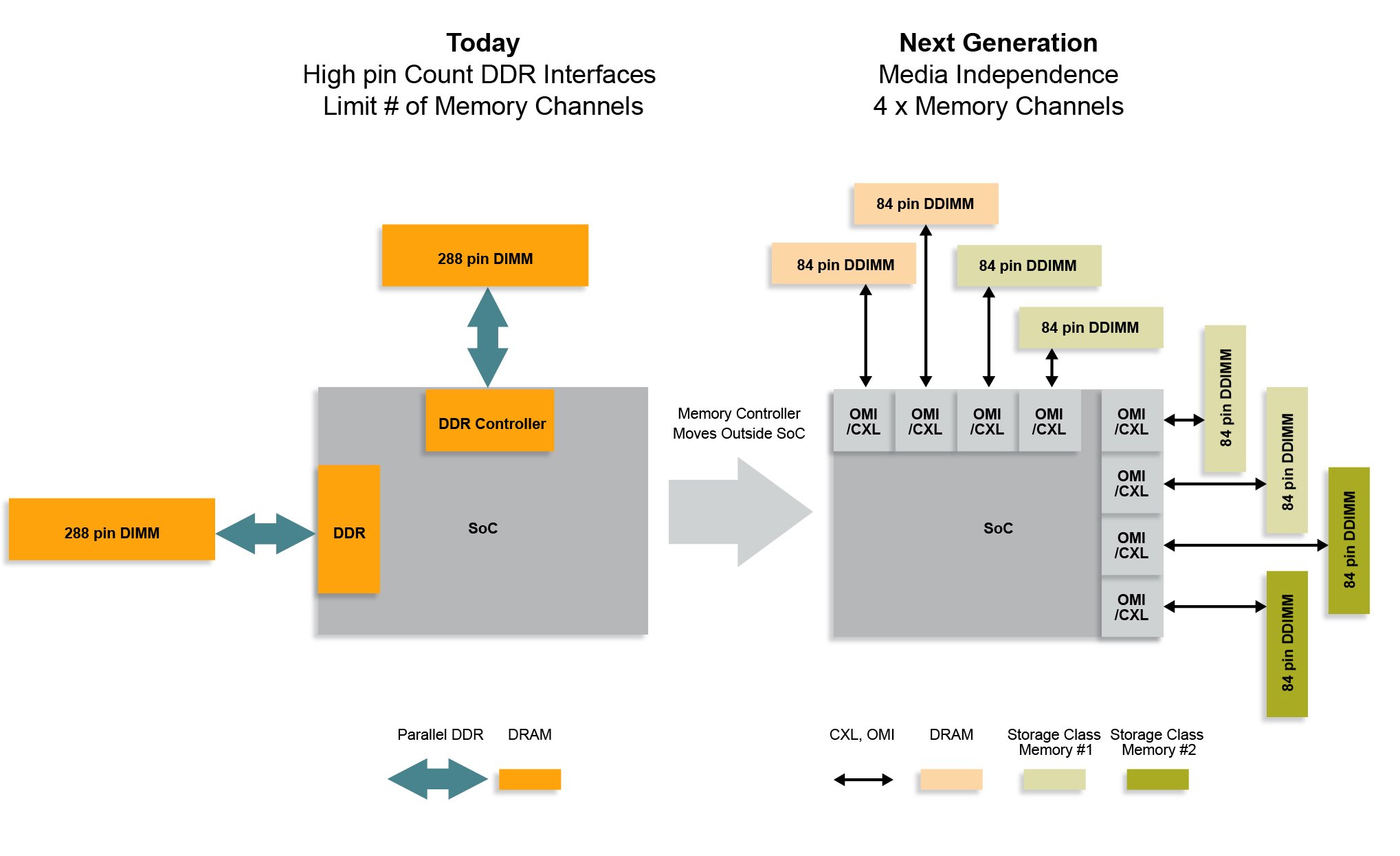
A broad range of silicon SoC devices including main stream CPU processors, application specific artificial intelligence (AI) devices, network processors, and other application specific standard products (ASSP) can all benefit from innovations in memory hierarchy. Multiple examples of new memory interface technology such as Open Memory Interface (OMI), Compute Express Link (CXL), and Gen-Z have emerged. SoC devices adopting these memory interface technologies can increase the number of independent memory channels while using far fewer SoC pins and therefore reduce the cost of SoC packaging. These new interface technologies also are media independent. System builders can change the cost and performance profile of their deployed equipment by changing the type of media connected to these SoC interfaces. This type of SoC memory direct attachment is called near memory technology.
Figure 2: New Components and Composable Infrastructure
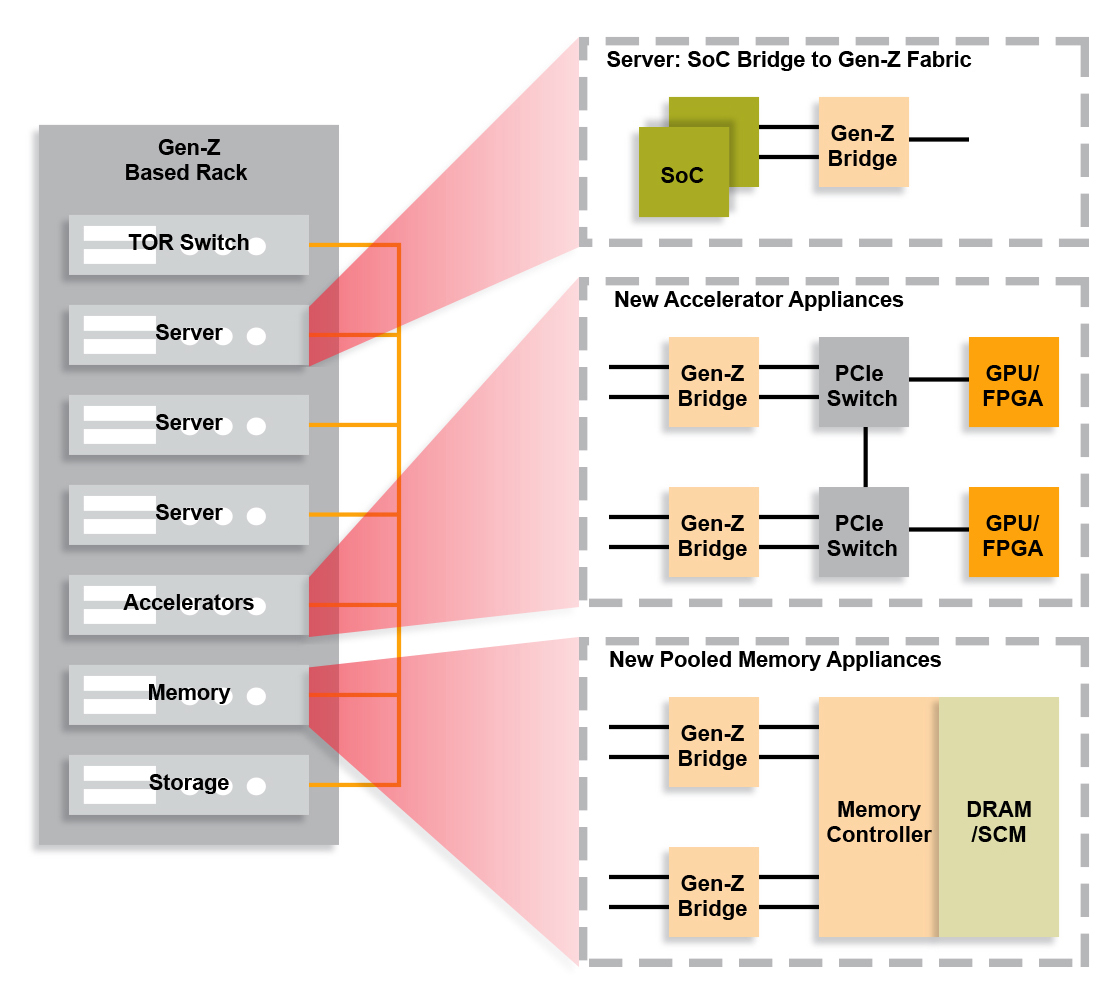
Near memory interface technologies can be used as on-ramp bridge interfaces to new memory interface technologies such as Gen-Z which include routable fabric support. Gen-Z supports “far memory pools” which can be shared at the rack level and beyond. Simultaneous and shared access to pools of ‘far memory’ can dramatically improve the performance of data-centric computing, real-time analytics performance, high performance compute (HPC) and machine learning application at the server cluster scale all the way up to warehouse scale computer (WSC) data center scale.
Microchip is a technology leader in the new memory infrastructure class of solutions offerings.
|
|
||||||||
 |
|||||||||